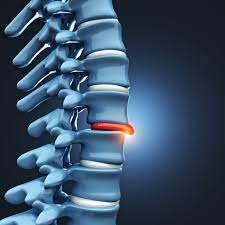
What Is the Fastest Way to Heal a Herniated Disc?
Back pain can be debilitating, and one of the primary culprits is a herniated disc. Understanding the nature of a herniated disc, its symptoms, and the best ways to treat it can make a world of difference for those affected. Let's dive deep into the details of this common ailment and explore potential treatments and preventive measures.
How to Heal a Herniated Disc Quickly?
A herniated disc occurs when the soft center of a vertebral disc, known as the nucleus, seeps out through a tear in the spinal column's casing. While there's no immediate remedy for a herniated disc, certain measures can foster faster healing. These include:
Rest: Give your back a break. Avoid activities that cause pain or strain.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can be beneficial.
Heat and Cold: Alternate between applying heat and cold to the affected area.
Stay Active: Gentle walks can prevent stiffness.
Alternative Treatments: Consider therapies like acupuncture, massage, or chiropractic care.
Medical Interventions: If home treatments don't alleviate symptoms, consult with a specialist. Options can range from corticosteroid injections to surgery, depending on the severity.
Symptoms
Herniated disc symptoms can manifest differently depending on the disc's location. Common indicators include:
Pain
Tingling
Numbness
Weakness
A herniated disc in the upper back or neck might result in symptoms in the arms or neck. Conversely, if it's in the lower back, symptoms might be felt in the hips or legs. Typically, symptoms intensify with activity and alleviate with rest.
Who is at Risk?
Certain individuals are more susceptible to herniated discs:
Those engaged in repetitive motions, especially involving lifting or twisting.
Drivers, due to prolonged sitting and vibrations from the vehicle.
Individuals with a genetic predisposition to disc issues.
Overweight individuals or smokers.
Men between the ages of 20 and 50 face the highest risk.
When to See a Doctor?
While mild back pain can often be managed at home, it's crucial to see a medical professional if:
The pain severely impedes daily activities.
Symptoms persist beyond six weeks.
Mobility is compromised.
Symptoms progressively worsen.
Loss of bladder or bowel control.
Tingling, numbness, or weakness in limbs.
How Do Doctors Diagnose?
Medical practitioners employ various diagnostic tools to pinpoint the cause of back pain:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides a detailed image of the spine, revealing abnormalities.
X-rays: Occasionally, herniated discs are found incidentally during unrelated x-rays.
Computed Tomography (CT): Focuses on the bones of the spine.
Myelogram: Uses contrast dye to identify spinal canal narrowing.
Electromyogram: Pinpoints affected nerves.
Prevention
Prevention is better than cure. Adopting certain lifestyle habits can reduce the risk of a herniated disc:
Strengthen Your Core: Engage in exercises that bolster abs, back muscles, and glutes.
Mind Your Posture: Always sit upright and ensure you lift objects with your legs and not your back.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra pounds can strain your spine.
Regular Stretching: Especially if sedentary for extended periods.
Quit Smoking: Nicotine can deteriorate spinal discs.
Conclusion
Herniated discs, while common, can greatly impede daily life. Being armed with knowledge and understanding the best ways to treat and prevent such conditions can pave the way for a healthier, pain-free life. If you or a loved one suspect a herniated disc, seek medical attention and take proactive measures towards recovery and prevention.